Constructing your dream frame house requires careful planning and attention to detail, regardless of your experience level.
This guide offers essential tips for a smooth and successful building process.
Planning Your Frame House
Constructing a frame house begins long before the first nail is hammered. A well-thought-out plan is your roadmap to success.
- Comprehensive Design: Work with an architect or a designer to create detailed blueprints. These plans should include every aspect of your house, from the layout to the electrical wiring.
- Budgeting: Develop a realistic budget. Consider the costs of materials, labor, permits, and unexpected expenses.
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline. Factor in weather conditions, material delivery times, and potential delays.
For detailed examples of modern frame house designs and inspirations, visit Carlisle Homes.
Choosing the Right Materials
Selecting quality materials is essential for the durability and aesthetics of your frame house.
- Wood Quality: Opt for high-quality lumber. It should be straight, free of large knots, and properly treated to resist moisture and pests.
- Insulation Options: Good insulation is key for energy efficiency. Research the best options for your climate.
- Exterior Finishes: Choose durable and weather-resistant materials for the exterior. This can range from traditional wood siding to modern composite materials.
Obtaining Necessary Permits
Securing the right permits is a critical step that should not be overlooked.
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local building codes and regulations.
- Permit Process: Start the permit application process early. Delays in obtaining permits can set back your entire project.
Laying the Foundation
Groundwork and Excavation
A sturdy foundation is the bedrock of any frame house.
- Site Preparation: Clear and level your building site. Remove any debris, rocks, or vegetation that might interfere with the foundation.
- Excavation: Dig the foundation according to your house plans. Ensure proper depth and width as per structural requirements.
Pouring the Foundation
The type of foundation you choose will depend on your location and budget.
- Slab-on-Grade: This is a popular choice for warmer climates. It involves pouring concrete directly on the ground.
- Crawlspace or Basement: In colder climates, a crawlspace or basement is common. This requires more excavation but offers additional living or storage space.
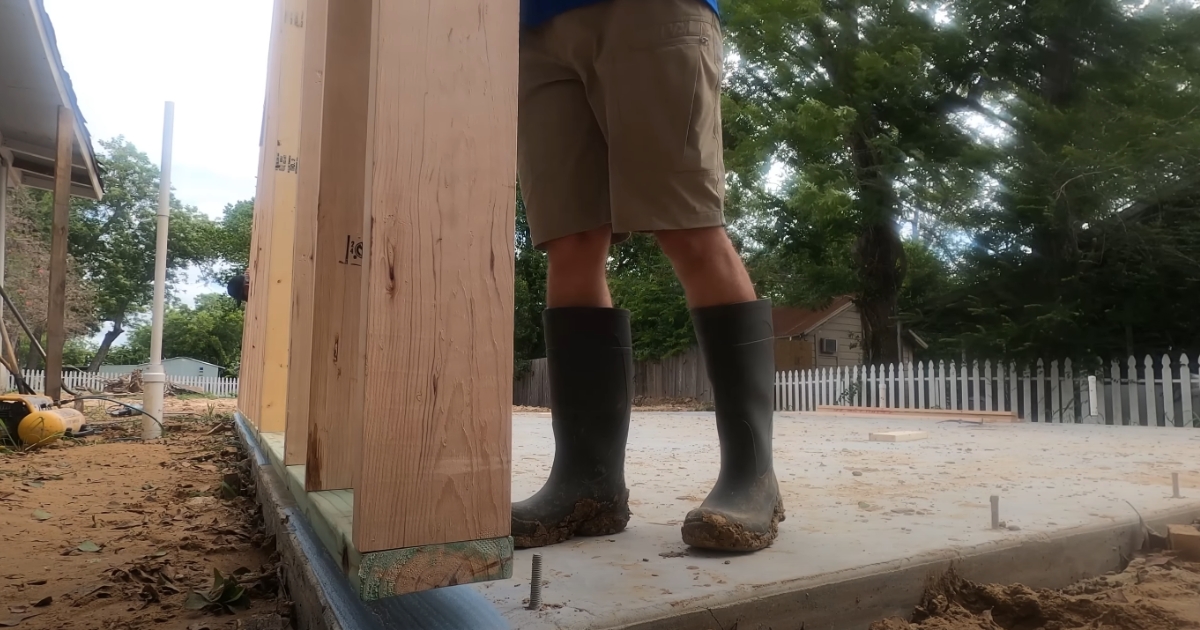
Ensuring Stability
The foundation must be level and stable to support the weight of the house.
- Reinforcement: Use steel bars or mesh to reinforce the concrete.
- Curing Time: Allow adequate time for the foundation to cure before starting the framing.
Constructing the Frame
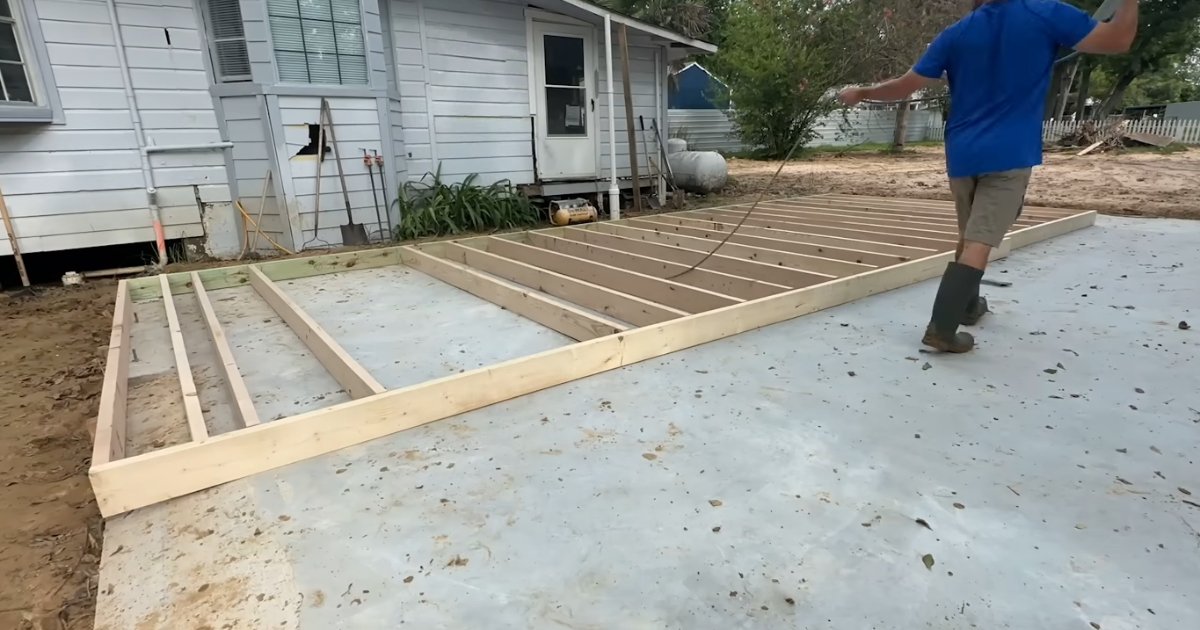
Building the Floor System
The floor system is the first part of the frame to be constructed.
- Joists and Beams: These form the main support for your floor. Ensure they are properly spaced and secured.
- Subflooring: Plywood or oriented strand board (OSB) is commonly used as subflooring. It should be laid down and secured to the joists.
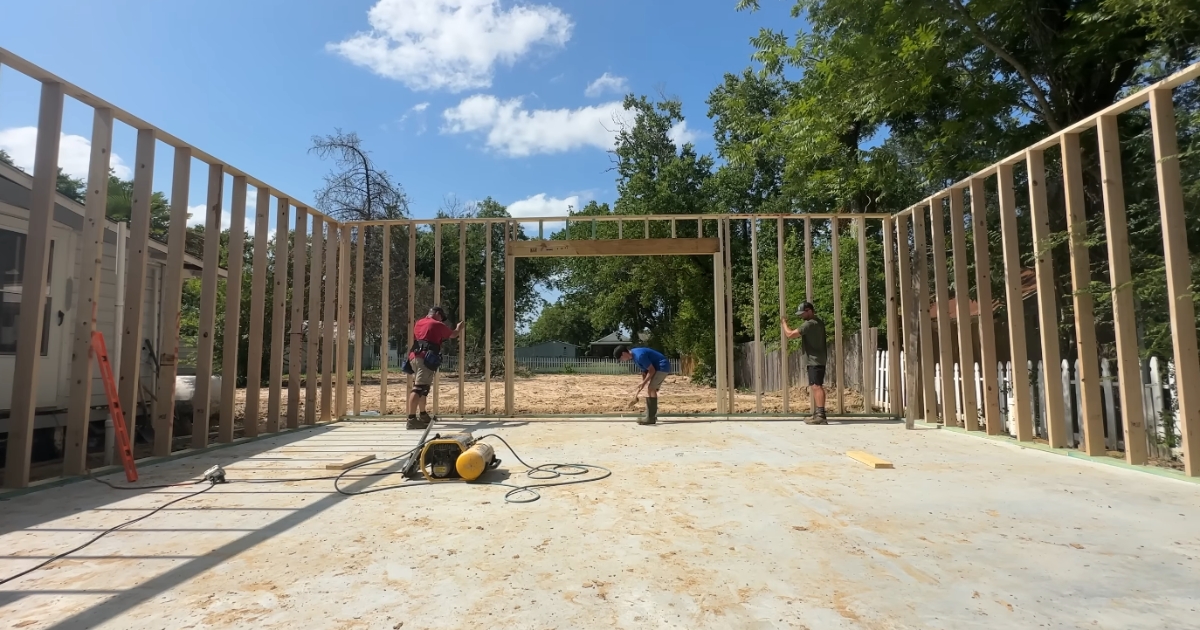
Erecting Walls
Walls are the vertical components of the frame and are crucial for the structural integrity of the house.
- Wall Framing: Assemble the wall frames on the ground and then lift them into place.
- Securing Walls: Ensure the walls are properly anchored to the foundation and each other.
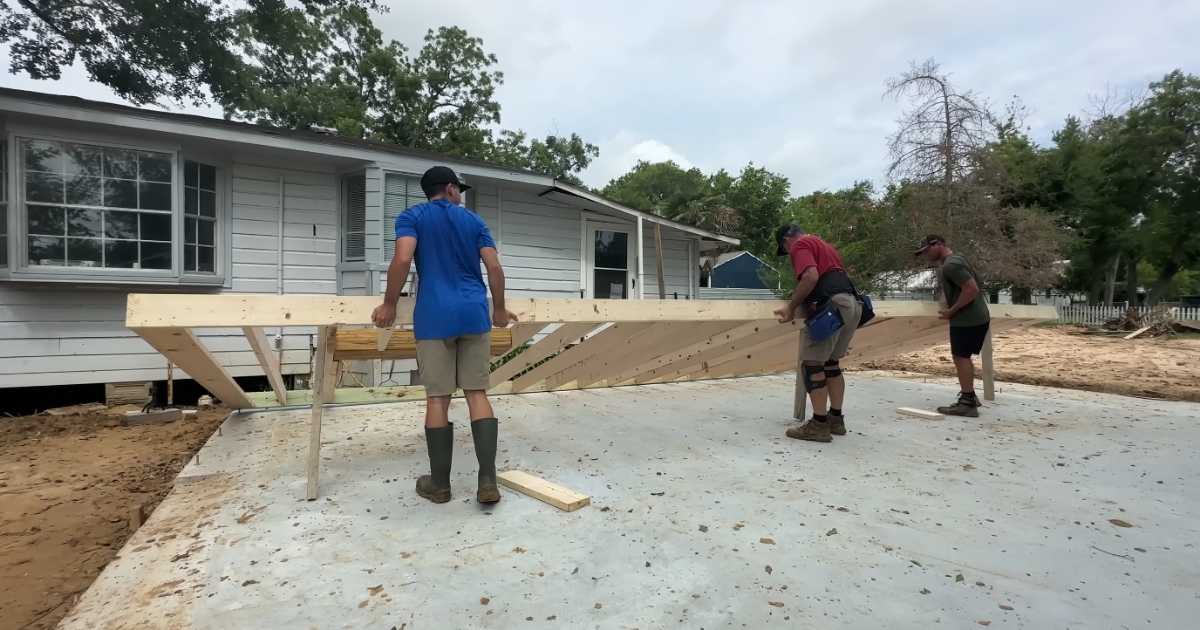
Adding the Roof
The roof protects your house from the elements and completes the basic structure.
- Trusses vs. Rafters: Decide between trusses (pre-made) or rafters (built on-site) for your roof structure.
- Sheathing and Roofing Material: Once the roof structure is in place, add sheathing and choose a durable roofing material.
Finishing Touches
Exterior and Interior Work
With the frame in place, you can start on the exterior and interior finishes.
- Siding and Windows: Install the chosen exterior finishes and windows.
- Drywall and Painting: Inside, hang drywall, apply joint compound, sand, and paint.
Installing Systems
The mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems are integral to making your house functional.
- Plumbing and Electrical: Hire licensed professionals to install these systems.
- Heating and Cooling: Install a suitable HVAC system for your climate.
Final Touches
Add the final touches to turn your construction into a home.
- Flooring and Cabinets: Install flooring materials, cabinets, and other fixtures.
- Landscaping: Finish with landscaping to enhance the curb appeal.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Anticipating and Managing Setbacks
In any construction project, challenges are inevitable. Being prepared can help you navigate these obstacles effectively.
- Weather Delays: Plan for weather-related delays, especially in seasons prone to rain or snow.
- Material Shortages: Have a backup plan for material shortages. Establish good relationships with multiple suppliers.
- Labor Issues: Ensure you have a reliable team. Consider contingency plans in case of labor shortages or disputes.
Quality Control and Inspections
Regular inspections and quality control are vital to ensure your frame house is built to standard.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule inspections at various stages of the construction process.
- Hiring Experts: Consider hiring a construction manager or an independent inspector for unbiased quality control.
- Addressing Issues Promptly: If problems are identified, address them immediately to avoid compounding issues.
Budget Management
Staying within budget is one of the most challenging aspects of any construction project.
- Track Expenses: Keep a detailed record of all expenses.
- Contingency Fund: Allocate a portion of your budget for unexpected costs.
- Cost-Saving Measures: Look for ways to save without compromising on quality. This could include comparing prices or choosing alternative materials.
Interior Design and Efficiency
Maximizing Space and Functionality
The interior design of your frame house should be both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
- Efficient Layout: Design a layout that maximizes space and suits your lifestyle.
- Storage Solutions: Incorporate ample storage to keep your home organized and clutter-free.
- Natural Light: Utilize large windows and strategic placement to maximize natural light.
Personalization
Adding personal touches will make your house feel like a home.
- Custom Features: Consider custom features that reflect your personality and style.
- Color Scheme: Choose a color scheme that creates the desired mood and atmosphere.
- Landscaping and Outdoor Spaces: Design outdoor spaces that complement the interior and provide additional living space.
Post-Construction Considerations
Maintenance and Upkeep
After construction, regular maintenance is key to keeping your frame house in top condition.
- Routine Checks: Regularly check for issues like leaks, cracks, or wear and tear.
- Seasonal Maintenance: Perform seasonal maintenance tasks such as gutter cleaning, HVAC servicing, and roof inspections.
- Record Keeping: Keep a record of all maintenance activities and warranties.
Insurance and Warranties
Protect your investment with the right insurance and understand the warranties on your home.
- Homeowner’s Insurance: Choose a comprehensive insurance policy that covers common risks.
- Warranty Awareness: Be aware of the warranties on your home’s components and how to make claims if necessary.
Community Integration
Becoming part of your new community can be a fulfilling aspect of building a new home.
- Neighborhood Involvement: Get involved in local events and organizations.
- Building Relationships: Introduce yourself to neighbors and build relationships.
- Respect Local Norms: Be mindful of local customs and norms to integrate smoothly into the community.
FAQs
Can I build a frame house on any type of land?
No, not all land is suitable for building a frame house. Factors such as soil stability, topography, and local climate must be considered. It’s advisable to conduct a land assessment before purchasing a plot for construction.
How long does it typically take to build a frame house?
The timeline varies depending on the size and complexity of the house, but generally, it takes about 4-6 months from start to finish for a standard frame house.
Are frame houses energy-efficient?
Frame houses can be energy-efficient when designed with features such as adequate insulation, energy-saving windows, and eco-friendly materials.
What’s the average cost per square foot for building a frame house?
Costs for building a frame house typically range from $100 to $200 per square foot, varying with location, materials, and design complexity.
Is it possible to expand a frame house after it’s built?
Yes, frame houses offer flexibility for future expansions. However, it’s important to consider potential expansion in the initial design phase and consult with an architect or builder.
Can I build a frame house in a cold climate?
Absolutely. Frame houses can be built in cold climates, but they require specific design considerations like higher R-value insulation, efficient heating systems, and weatherproofing to handle the colder conditions.
Final Words
Building a frame house is a complex but achievable project. Adhering to these guidelines and focusing on details guarantees a smooth construction process.
Keep in mind that meticulous planning, superior materials, and expert craftsmanship are essential for creating your dream frame house.