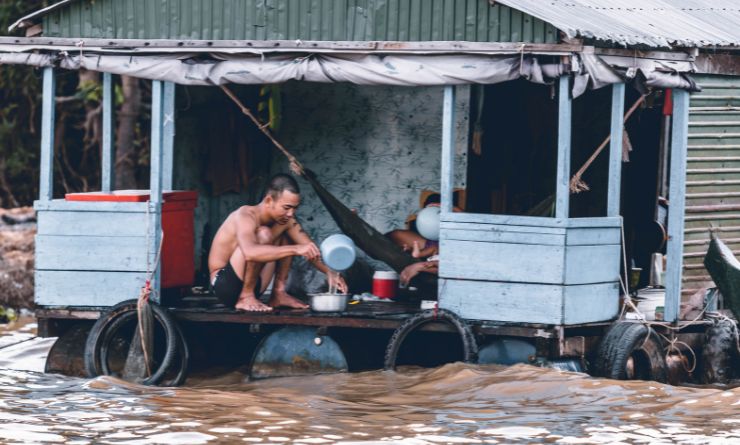
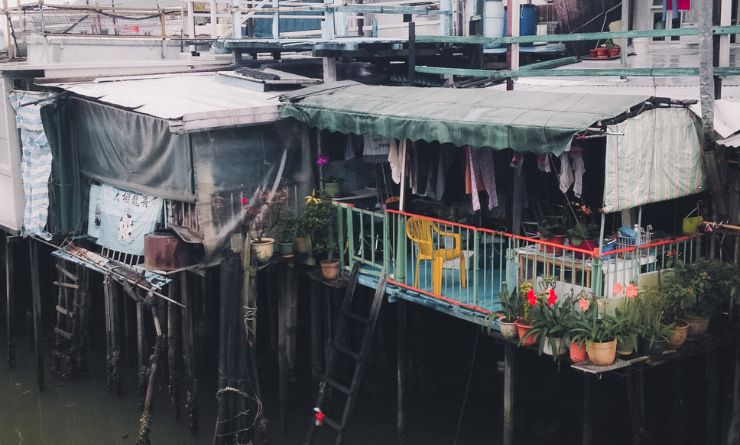
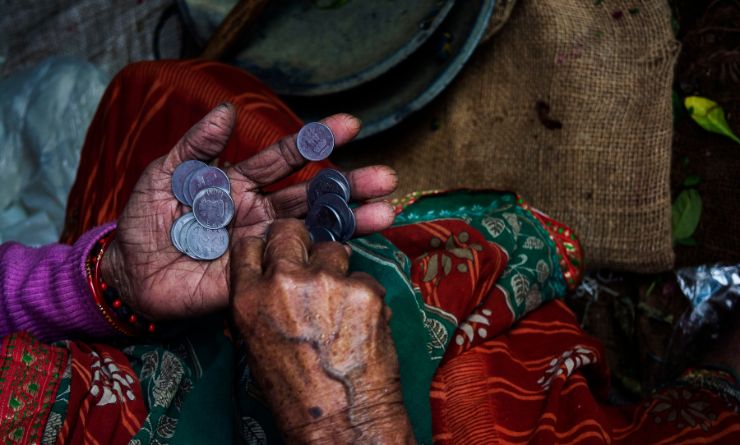
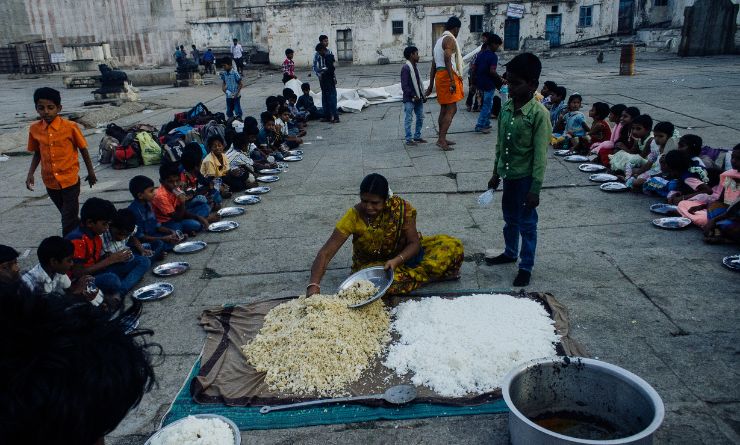
The issue of poverty remains a significant global challenge, with many countries struggling to improve the living conditions of their population. This article delves into the topic of the poorest countries in the world, examining the factors that contribute to their poverty and the efforts being made to alleviate it.
Poverty is a complex issue that encompasses various economic, social, and political factors. In this article, we will explore the poorest countries and their unique circumstances. Understanding the causes and implications of poverty is vital in creating effective strategies to address this global issue.
Factors to Determine Poorest Countries
To determine the poorest countries, several indicators are considered, primarily focusing on economic and social aspects. Economic indicators, including income levels, GDP per capita, and unemployment rates, provide insights into a country’s economic well-being. Social indicators, such as access to education, healthcare services, and basic amenities, shed light on the social conditions within these countries. The Human Development Index (HDI) provides a comprehensive measure of a country’s overall development and standard of living.
List of Poorest Countries in the World:
Examining the data, we will explore the regions with the highest concentration of poorest countries. Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Central America and the Caribbean are recognized as regions with a significant number of countries facing extreme poverty. We will delve into the specific countries within these regions and the challenges they face.
Causes of Poverty in the Poorest Countries:
Poverty is a result of various interconnected factors. Political factors, including corruption, inadequate governance, and instability, can hinder economic growth and development. Economic factors such as lack of infrastructure, limited access to resources, and unequal distribution of wealth contribute to the cycle of poverty. Geographical constraints, such as landlocked locations or vulnerability to natural disasters, can also impact a country’s economic prosperity.
Efforts to Alleviate Poverty in the Poorest Countries:
Recognition of the urgent need to address poverty has led to various efforts to alleviate it. International aid and assistance programs play a vital role in providing financial and technical support to these countries. In addition, governments implement programs and policies aimed at poverty reduction, focusing on education, healthcare, and economic empowerment. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and initiatives also contribute by implementing grassroots projects and providing support to vulnerable communities.
By examining the poorest countries, their causes of poverty, and the efforts being made to combat it, we can gain a deeper understanding of this global issue and work towards creating a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
Factors to Determine Poorest Countries
When examining the factors that determine the poorest countries, we can explore various indicators that shed light on their economic conditions, social well-being, and overall human development. Join me as we uncover the intricate web of data and statistics that help us understand the dire circumstances faced by these nations. From economic indicators to social metrics and the human development index, we’ll unravel the complexities that contribute to their current predicament and gain a deeper insight into the reality of poverty around the world.
Economic Indicators
These economic indicators provide insights into a country’s financial health. Low GDP and GNI per capita, high unemployment rates, and inflation rates, as well as a lack of foreign direct investment, indicate economic struggles. It’s important to note that these economic indicators alone do not fully capture the complexities of poverty. Social indicators and the Human Development Index also play a significant role in understanding the well-being and living conditions of these countries.
Social Indicators
Access to clean water is crucial for a healthy population as it helps prevent the spread of diseases. A higher percentage of people with access to clean water indicates better sanitation infrastructure and improved public health.
The poverty rate reflects the percentage of the population living below the poverty line. A lower poverty rate indicates a higher standard of living and greater economic stability.
When assessing social indicators in the poorest countries, it is important to consider these factors along with economic indicators and the Human Development Index. Addressing poverty requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on improving education, healthcare, and access to basic amenities.
Analyzing social indicators allows policymakers and organizations to identify areas that require attention and take targeted actions to alleviate poverty.
Suggestions for improving social indicators in the poorest countries include investing in education and promoting literacy programs, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, improving access to clean water and sanitation facilities, and implementing social welfare programs aimed at reducing poverty and improving living conditions for vulnerable populations.
By addressing these social indicators, countries can work towards reducing poverty and improving the well-being of their citizens.
Discover why some countries have a long way to go when it comes to human development, and how the Human Development Index captures the struggle in one number.
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a crucial indicator used to measure the well-being and development levels of countries. The HDI considers factors like life expectancy, education, and income per capita to assess a country’s development.
Life expectancy is a significant factor in the HDI, reflecting the overall health and quality of life. Countries with higher life expectancies tend to have better healthcare systems and higher standards of living. Japan and Switzerland consistently rank high on the HDI due to their high life expectancy.
Education is another essential component of the HDI. Access to quality education enhances human capital and boosts productivity. Countries that prioritize education, like Norway and Australia, often rank well on the HDI.
Income per capita is a crucial economic indicator used to calculate the HDI. It represents the average income of individuals within a country and reflects economic development and standard of living. Countries with high income per capita, such as Luxembourg and Qatar, often rank high on the HDI.
By considering indicators like life expectancy, education, and income per capita, the HDI provides a comprehensive assessment of a country’s development. It offers valuable insights into well-being and potential for growth, serving as a useful tool for policymakers and researchers.
The HDI has limitations. It doesn’t capture aspects like inequality within a country or environmental sustainability. It also may not adequately consider cultural, social, and political factors.
Despite these limitations, the HDI remains a widely recognized and valuable tool for understanding and comparing development levels. It helps highlight disparities and identify areas for improvement. Through a holistic analysis of life expectancy, education, and income per capita, the HDI provides a comprehensive picture of development status and guides policymakers in enhancing well-being and achieving sustainable development.
List of Poorest Countries in the World
Among the nations grappling with economic challenges, there are several that stand out as the poorest countries in the world. The sub-sections of this article will take you on a tour through Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Central America and the Caribbean, shedding light on the struggles faced by these regions. Brace yourself for a glimpse into the harsh realities and stark disparities that prevail in these areas, as we explore the socio-economic landscapes of the world’s poorest countries.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is a region in Africa known for high poverty levels and economic challenges. It consists of countries south of the Sahara Desert. Political instability, economic factors, and geographical constraints are all contributors to poverty in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Political instability: Frequent conflicts, corruption, and weak governance make it difficult for these countries to develop their economies and provide essential services to their populations.
- Economic factors: Many Sub-Saharan African countries heavily rely on vulnerable agriculture, which is affected by climate change and external shocks. Limited access to capital, financial resources, and low industrialization also hinder economic growth in the region.
- Geographical constraints: Sub-Saharan Africa faces challenges such as being landlocked, limited access to natural resources, and unfavorable climatic conditions. These constraints hinder infrastructure development and economic growth.
Efforts to alleviate poverty in Sub-Saharan Africa include international aid, government programs, and NGOs. Organizations like the United Nations and the World Bank provide financial and technical support. Governments implement poverty reduction strategies and social welfare programs. NGOs and grassroots initiatives provide basic services, education, healthcare, and livelihood opportunities.
Although Sub-Saharan Africa has faced challenges, some countries have made significant progress in reducing poverty rates and improving human development indicators. Sustainable development and poverty eradication require continued efforts and investments in education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and economic diversification. By addressing root causes and fostering inclusive growth, Sub-Saharan Africa can improve well-being and livelihoods.
Asia
In Asia, some countries are among the world’s poorest. Here is a table of these countries and their GDP per capita:
| Country | GDP per capita (USD) |
| Afghanistan | 628 |
| Bangladesh | 1,909 |
| Cambodia | 1,672 |
| Laos | 2,499 |
| Myanmar | 1,350 |
| Nepal | 1,155 |
| Pakistan | 1,518 |
These countries face challenges in economic development and social welfare. Factors like political instability, economic inequality, and geographical constraints contribute to their poverty.
Efforts to reduce poverty involve international aid, government programs, non-governmental organizations, and initiatives. They aim to improve living conditions, education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Governments in Asia implement social welfare programs, microfinance initiatives, and job creation schemes to enhance well-being and economic opportunities.
Poverty in Asia is a complex issue, requiring concerted efforts to address causes and facilitate sustainable development. By improving economic and social indicators, and fostering human development, progress can be made in reducing poverty in Asia.
Central America and the Caribbean
face significant poverty challenges. Economic factors, social factors, and political factors all contribute to the high levels of poverty in this region.
- Economic Factors: Low income levels, high unemployment rates, and limited access to economic opportunities are challenges in Central America and the Caribbean. Many countries in this region heavily rely on agriculture, which lacks modern technology and is prone to climate-related disasters, leading to unstable incomes.
- Social Factors: Limited access to quality education and healthcare services perpetuate the cycle of poverty. Inadequate infrastructure and lack of basic services such as clean water and sanitation further hinder poverty reduction efforts.
- Political Factors: Political instability, corruption, and weak governance hinder development efforts. Political conflicts and social unrest negatively impact economic growth and poverty reduction initiatives in some countries.
Efforts to alleviate poverty in Central America and the Caribbean are crucial for improving the well-being and living standards of the population. Key initiatives include:
- International Aid and Assistance: International organizations and donor countries provide financial and technical assistance to support poverty reduction programs, improve infrastructure, and promote economic development in the region.
- Government Programs and Policies: Governments play a crucial role in poverty reduction through social protection programs, investment in education and healthcare, and the promotion of small-scale industries and entrepreneurship.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and Initiatives: NGOs and community-based organizations work towards poverty alleviation through interventions such as vocational training, microfinance services, and healthcare support.
Addressing economic, social, and political factors, along with effective implementation of targeted interventions, are necessary to make progress in lifting communities out of poverty and improving the overall well-being of Central America and the Caribbean.
Finding the causes of poverty in the poorest countries is like untangling a web; it’s messy, confusing, and you’ll probably get stuck.
Causes of Poverty in the Poorest Countries
In the realm of the world’s poorest countries, poverty exists due to a myriad of complex factors. This section investigates the causes that lead to such dire circumstances. Join us as we delve into the political, economic, and geographical constraints that contribute to the persistent poverty seen in these nations. Brace yourself for a revealing exploration that sheds light on the intertwined elements shaping the destitute conditions experienced by these societies.
Political Factors
Political factors play a vital role in determining poverty levels in the world’s most impoverished nations. These factors are closely interconnected with economic and social indicators, and they contribute to the continuation and exacerbation of poverty. Some key political factors that contribute to poverty are:
- Corruption: The pervasiveness of corruption within government institutions greatly obstructs the allocation of resources and undermines public services. It results in the mismanagement of funds designated for poverty alleviation programs and impedes economic growth.
- Weak governance: Inadequate governance structures coupled with limited accountability and transparency lead to ineffective policies and inadequate delivery of public services. Consequently, this exacerbates the marginalization of the poor and hampers their access to vital resources and opportunities.
- Political instability: Countries that experience political instability, characterized by frequent leadership changes or prolonged conflicts, face difficulties in implementing long-term development strategies. This instability hampers investment and economic growth, further worsening poverty rates.
- Limited participatory processes: A lack of citizen engagement and participation in decision-making processes can result in policies that fail to address the needs of the population, particularly vulnerable and marginalized groups. This perpetuates inequalities and impedes efforts to reduce poverty.
- Inadequate legal systems: Weak legal systems that fail to effectively enforce property rights and contracts hinder private sector development and discourage foreign investment. As a result, economic growth is restricted, and opportunities for poverty alleviation remain limited.
Addressing political factors is of utmost importance in achieving sustainable poverty reduction in the world’s poorest countries. Governments, international organizations, and civil society must collaboratively work together to combat corruption, strengthen governance structures, promote stability, enhance citizen participation, and establish robust legal frameworks. By effectively addressing these political factors, these nations can create an enabling environment for poverty reduction initiatives to thrive and ultimately lead to long-term, sustainable development.
Economic Factors
When examining economic factors in the poorest countries, it is crucial to consider key indicators. These indicators provide insight into economic challenges faced by these nations and help identify areas requiring intervention and support. The table below outlines significant economic factors affecting poverty in these countries:
| Factor | Description |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Measures the total economic output of a country, including goods and services produced within its borders |
| Income Inequality | Indicates the disparity in income distribution among the population, with higher levels of inequality resulting in increased poverty rates |
| Unemployment Rate | Reflects the percentage of the labor force that is jobless and seeking employment, revealing the difficulty in achieving income |
| Access to Financial Services | Examines the availability of banking services, credit, and microfinance opportunities, crucial for entrepreneurial activities and economic growth |
| Infrastructure Development | Refers to the quality and availability of roads, transportation networks, energy sources, and communication systems, vital for economic advancement |
These economic factors often intersect with political and geographical constraints, exacerbating poverty levels in the poorest countries. Political instability, corruption, and inadequate governance can hinder economic growth and impede poverty reduction strategies. Geographical limitations, such as landlockedness or vulnerability to natural disasters, can further impede economic development.
To alleviate poverty in the poorest countries, it is important to address these economic factors comprehensively. International aid, government programs and policies, and initiatives by non-governmental organizations play a crucial role in combating poverty. By focusing on sustainable economic development, promoting job creation, and fostering inclusive growth, these efforts can help uplift communities and improve the lives of people living in poverty.
Consider a small community in an impoverished country where access to financial services was non-existent. Upon the introduction of microfinance initiatives, individuals gained the opportunity to start their own businesses and generate income. As a result, the community experienced an economic transformation, with locals cultivating their entrepreneurial skills and creating a thriving local economy. This success story highlights the importance of economic factors in poverty alleviation and showcases the potential impact of targeted interventions.
Geographical Constraints
Geographical constraints contribute significantly to poverty levels in the poorest countries. These constraints limit economic development and well-being. Some constraints affecting these countries include:
- Limited access to resources: Some countries face difficulties accessing essential resources like water, fertile land, and minerals. For example, landlocked countries like Burkina Faso in West Africa lack direct access to ports, hindering trade and economic growth.
- Harsh climate conditions: Extreme climates, including arid deserts, drought-prone regions, and remote areas with rugged terrains, pose challenges for agriculture and infrastructure development. Countries like Niger in sub-Saharan Africa face recurrent droughts, making crop cultivation difficult and causing food insecurity.
- Vulnerability to natural disasters: Some countries are at a higher risk of natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods due to their geographical location. These disasters can cause significant damage to infrastructure, homes, and agricultural lands. Haiti, located in the Caribbean, is highly prone to hurricanes, hindering its development efforts.
- Lack of transportation infrastructure: Inadequate road networks, ports, and airports make efficient transportation of goods and people difficult. This limits trade opportunities, market access, and economic growth. In the poorest countries of sub-Saharan Africa, inadequate transportation infrastructure hampers regional integration and trade.
- Isolation and landlocked status: Some countries are geographically isolated or landlocked, depending heavily on neighboring countries for trade. This dependence leads to higher transportation costs and limited market access, hindering economic development. The landlocked country of Malawi in Southeast Africa faces challenges accessing international markets due to its geographic location.
- Limited natural resources: Some countries lack significant natural resources like oil, gas, or minerals, which impedes economic growth and development opportunities. The absence of such resources limits their revenue generation and employment creation.
Strategic planning, infrastructure development investments, and regional cooperation can help overcome these geographical constraints. By identifying and addressing these obstacles, countries can enhance their economic potential and improve the well-being of their citizens.
From international aid to government programs and NGOs, efforts to fight poverty in the poorest countries are a beacon of hope in an otherwise dark world.
Efforts to Alleviate Poverty in the Poorest Countries
Efforts to alleviate poverty in the poorest countries are multifaceted, involving international aid and assistance, government programs and policies, as well as non-governmental organizations and initiatives. Learn how these various approaches aim to combat poverty, improve living conditions, and foster sustainable development. Together, they form a global response driven by the shared goal of creating a more equitable and prosperous world for the most vulnerable populations.
International Aid and Assistance
International Aid and Assistance is crucial in alleviating poverty in the poorest countries. Here are some key points to consider:
- Humanitarian Aid: International aid provides immediate relief with food, water, shelter, and medical assistance during emergencies. Organizations like the Red Cross and UNICEF deliver humanitarian aid to those in need.
- Development Aid: International assistance focuses on long-term projects to address poverty. This includes funding for infrastructure, education, healthcare, and agriculture. Organizations like the World Bank support development projects in impoverished nations.
- Capacity Building: International aid enhances the capabilities of governments and local organizations in the poorest countries through technical expertise, training programs, and knowledge sharing. This improves governance, institutions, and economic management.
- Debt Relief: International financial institutions and donor countries provide debt relief to alleviate the burden on the poorest countries. This allows more resources for poverty reduction and development.
- Trade Assistance: International aid initiatives promote fair trade and economic growth in the poorest countries. This includes access to markets, trade infrastructure improvement, and support for export-oriented industries. Organizations like the World Trade Organization work towards creating a conducive trade environment.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: International aid involves collaboration between governments, NGOs, and the private sector. Partnerships ensure efficient delivery of aid and coordinated efforts for maximum impact.
Efforts must ensure effective utilization of international aid, targeting areas of greatest need and working closely with local communities for sustainable solutions. International aid and assistance can significantly uplift the poorest countries and improve the lives of millions.
Government Programs and Policies
Government programs and policies are crucial in addressing poverty in the poorest countries. These initiatives play a significant role in providing support, resources, and opportunities for those in need. Here are some examples of government programs and policies that can effectively alleviate poverty:
- Social welfare programs: Governments can implement programs that offer financial assistance to individuals and families who require it. These programs, such as cash transfers or social pensions, can help immediately reduce poverty by providing a safety net for those facing economic hardships.
- Education initiatives: Governments can prioritize education by implementing policies that ensure access to quality education for all. This includes initiatives like free or subsidized school fees, scholarships, and investments in educational infrastructure. Education is crucial in breaking the cycle of poverty and empowering individuals with knowledge and skills for better employment opportunities.
- Job creation programs: Governments can create programs that promote job opportunities and entrepreneurship. This can include incentives for businesses to invest in job creation, vocational training programs to enhance skills, and support for micro and small enterprises. By boosting employment opportunities, governments can help individuals and families escape poverty.
- Healthcare policies: Access to affordable and quality healthcare is vital in reducing poverty. Governments can implement policies that provide healthcare services and facilities in marginalized areas, health insurance schemes, and subsidies for healthcare costs for the poor. These measures ensure that individuals have access to essential healthcare services without facing financial burdens.
- Agricultural support: Many of the poorest countries rely on agriculture for their livelihoods. Governments can implement policies and programs that support small-scale farmers by providing access to resources such as land, seeds, and fertilizers. Investing in agricultural research, technology, and infrastructure can enhance productivity and improve farmers’ income.
Government programs and policies alone cannot fully solve the complex issue of poverty, but they play a crucial role in providing the necessary support and opportunities for impoverished individuals and communities. It is important for governments to continuously assess and evaluate these programs to ensure their effectiveness in addressing poverty and promoting sustainable development.
Non-Governmental Organizations and Initiatives
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and Initiatives play a crucial role in addressing poverty in the world’s poorest countries. They work alongside governments and stakeholders to implement programs and provide support. Here are key factors to consider when looking at the impact of NGOs and Initiatives in poverty reduction:
- Targeted interventions: NGOs and Initiatives focus on specific areas of need like education, healthcare, clean water, and food security. They tailor programs to address unique challenges faced by communities in the poorest countries.
- Grassroots approach: These organizations work directly with local communities to understand their needs. This ensures culturally appropriate and sustainable interventions.
- Capacity building: NGOs and Initiatives not only provide immediate assistance but also prioritize skills training and entrepreneurship support. They empower individuals and communities to break the cycle of poverty.
- Advocacy and policy influence: These organizations advocate for policy changes at various levels. They raise awareness about the root causes of poverty and campaign for equality, social justice, and inclusive development.
- Collaboration and partnerships: NGOs and Initiatives collaborate with governments, international organizations, and stakeholders to maximize their impact. By leveraging resources and expertise, they can reach more people and implement sustainable solutions.
- Accountability and transparency: Many NGOs and Initiatives adhere to high standards of transparency and accountability. They undergo monitoring and evaluation processes to measure their impact.
- Innovation and adaptation: NGOs and Initiatives continually innovate and adapt to emerging challenges. They incorporate new technologies, research findings, and best practices to improve their interventions.
By considering these factors, individuals and organizations can make informed choices when supporting or collaborating with Non-Governmental Organizations and Initiatives working towards poverty reduction. These organizations drive positive change and create a more equitable and prosperous world.
FAQs
What are the primary methods used to determine the world’s poorest countries?
The world’s poorest countries are typically classified as low-income economies based on their Gross National Income (GNI) per capita. GNI is the total income generated by a country, including income from international sources, divided by its population. Countries with a GNI of less than $1,046 (adjusted to current US dollars) are considered low-income.
This figure is used to assess the financial standings of nations and identify the poorest countries. Factors such as life expectancy at birth and the level of education are considered in reports like the United Nations Human Development Report to determine poverty rankings.
Why are the majority of the world’s poorest countries located in Sub-Saharan Africa?
Sub-Saharan Africa is home to a significant number of the world’s poorest countries due to several factors. These include institutional weakness, corruption, poor infrastructure, and a lack of human capital. These challenges have hindered economic development and contributed to a lower overall quality of life for citizens in these countries.
It is worth noting that the region also houses some of the fastest-growing economies in the world, indicating potential positive signs for the future.
What are the specific challenges faced by the top five most impoverished countries in the world?
The top five most impoverished countries in the world, according to projections, are Somalia, South Sudan, Sierra Leone, Malawi, and the Central African Republic. These countries face various challenges that contribute to their poverty. For example, Somalia is plagued by violence and is combating the Islamist insurgency group Al-Shabab. South Sudan’s economy is fragile due to a civil war, food insecurity, and supply disruptions.
Sierra Leone is recovering from a civil war and limited fiscal space. Malawi relies heavily on subsistence agriculture and faces high public debt and vulnerability to extreme weather events. The Central African Republic faces a weak central government, armed rebel groups, and economic instability due to its reliance on natural resources.
How does extreme poverty affect the lives of individuals in the world’s poorest countries?
Extreme poverty, prevalent in the world’s poorest countries, has profound impacts on individuals and communities. It can limit access to basic necessities such as food, clean water, healthcare, and education.
People living in extreme poverty often struggle to maintain a decent standard of living and are more vulnerable to adverse conditions such as natural disasters and conflicts. The fight against poverty relies on providing tools and resources to uplift and empower individuals, communities, and countries.
What are the social and economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world’s poorest countries?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had severe social and economic consequences for the world’s poorest countries, exacerbating existing challenges. These countries, already facing high rates of poverty, have experienced soaring inflation, disrupted supply chains, and increased vulnerability.
The pandemic has also led to job losses, reduced incomes, and disrupted education systems. The World Bank predicts that the current generation of students in these countries could lose up to 10% of their future average annual income. The IMF estimates that an additional 198 million people have likely entered extreme poverty since the onset of the health emergency.
How does the war in Ukraine impact food insecurity in the world’s poorest countries?
The war in Ukraine has led to higher food prices, which further exacerbates food insecurity in the world’s poorest countries. These vulnerable countries already face challenges such as drought conditions, climate change, and limited resources.
The IMF predicts that an all-time high of 345 million people across 79 countries will face acute food insecurity in 2024. Resolving conflicts and addressing the underlying causes of global food insecurity is crucial in improving the living conditions of people in the world’s poorest nations.